Hendrik Vanlon Smith Jr said “When new things emerge in our world, it's best to put some time into researching them and trying to gain an understanding. With that understanding, you're then able to think about and plan for the new business applications for those things and the new ways in which your business may profit from them.”
Heavy investments from top brands like Google, Amazon, Facebook, Microsoft, etc, already understand this and have spiked the interest of the ordinary man walking the street with his favorite magazine as they continue to make headlines and front pages with their multi-million dollar investment in the metaverse. Now the question is, what exactly is this Metaverse?
Metaverse is not a new concept as people view it. Metaverse has lived long since the 1960s and ’70s. Morton Heilig invented the first ever VR system in 1962 “the Sensoama” and the very first virtual reality game “MUD” of 1978 started what we know today as the metaverse. However, Metaverse only just became a brand identity by 1992 after appearing in Stephen Neil’s Novel “Snow Crash”. Metaverse gained traction with recent innovations and enhancements in past technologies. This enhancement has caught the attention of the world's top business tycoons as the most pronounced use case. Resulting in exponential market value in coming years. Bloomberg Intelligence analysis reports Metaverse's value is estimated to reach $800 billion market by 2024 with projected numbers of $5 trillion by 2030.
The idea behind Metaverse is a mix of creativity and the universe- The word “meta” serves as creativity and “verse” as the universe. Since the metaverse is defined as a virtual world, you will agree that creativity is one component of the world, and technology since the age of man has proven to be extremely useful in its evolution.
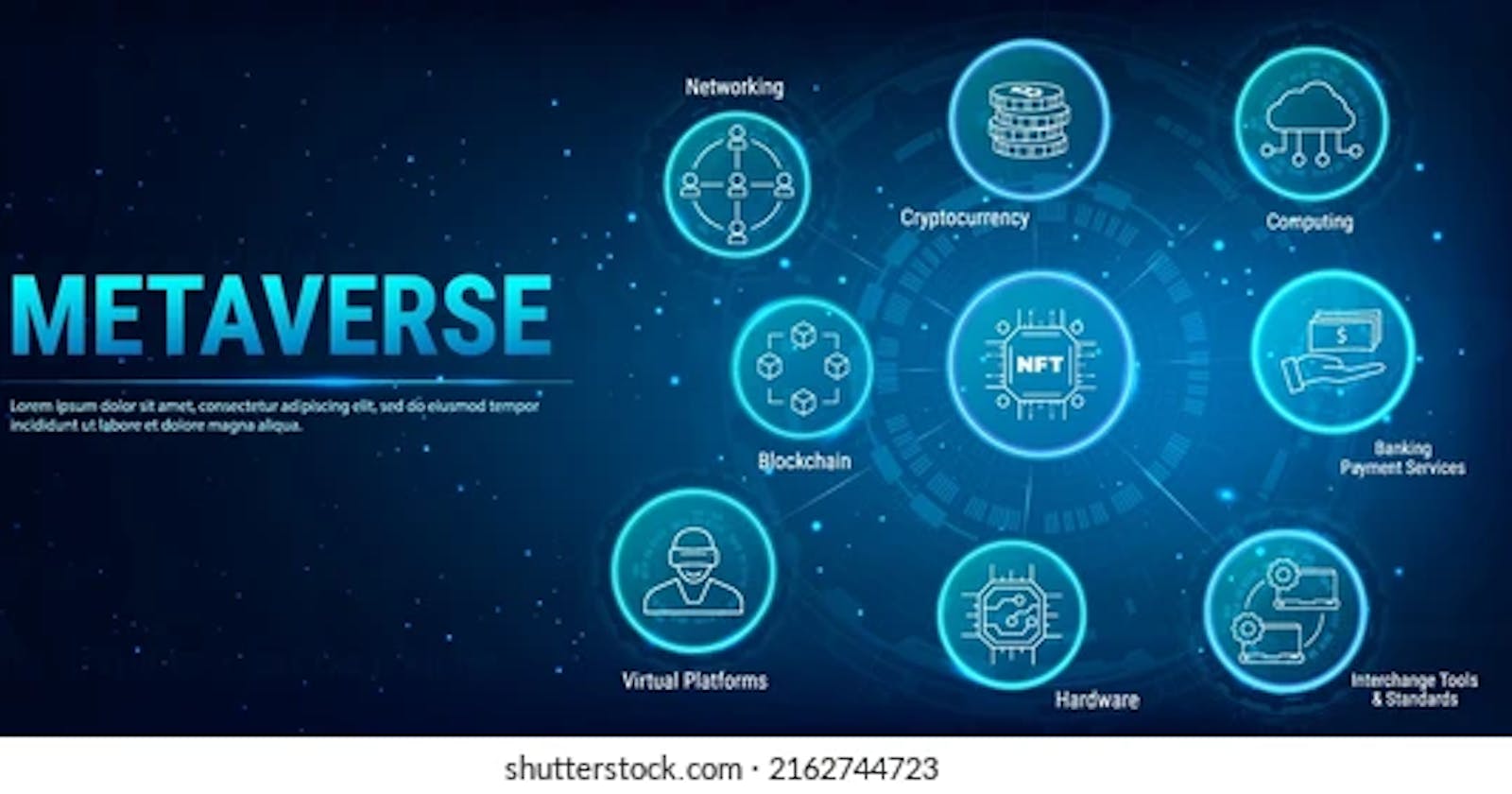
However, the question of what technology power the Metaverse is a widely asked one as steady evolution continues. While there are no standard categories to section these technologies, metaverse can be grouped into two categories, hardware, and software applications/devices.
Hardware Devices that support the Metaverse
The Metaverse infrastructure is designed to run hardware devices that create the virtual world immersive effect when worn and allow the human imagination to run wild. According to reports, One of the most commonly used hardware devices in the metaverse, the “VR headset” is expected to reach a market value of $89 billion in coming years.
Virtual Reality (VR) Headset:
The VR headsets come in form of helmets or glass straps and are accompanied by two-hand controllers with embedded digital graphics. When worn, they help to visualize and interact with a 3D-generated virtual environment and allow users to revel in their human-like experience. With VR, people are capable of carrying out sequential simulation movements and manipulation of items in a digital environment with their avatars, enabling them to explore their human senses and aid in creating new styles of communication and understanding of the virtual world geared towards enhancing knowledge in gaming, education, training, etc. The most recent Facebook(Now Meta) “Quest 2” is one such device.
Augmented Reality (AR)/Mixed Reality gadgets:
As its name implies, augmented Reality (AR) or Mixed Reality gadget serves as a supportive relay of a digital and real-life world. Augmented reality allows users to feel a combined world of Factual and virtual content present in a physical environment. Several AR devices are present today, such as digital wearables and Hologram projectors. Holograms are 3D photographic digital representations categorized into transmission holograms and reflection holograms. The reflection hologram allows mixed demonstration and interaction with digital entities by directly gazing at the screen hovering in the air, and tapping in on the distributed informationation in the real world while also viewing virtual objects and information without the need to wear a headset. Examples of AR are Microsoft hololens, Google Smart glass, and Samsung smart Glass.
5G or Low Tenancy Server Tower:
Internet connectivity is an important aspect of the world. With the evolution of the internet from web1 to web2 to a more advanced web recently called web3, this web is intended to connect the social networks of the metaverse to users globally. 5G technology solves the need for faster networks with lower latency to enable vastly more connected devices to process data, including VR headsets or AI-powered bots that will open up experiences and allow visitors to have in-depth conversations with the virtual world.
EDGE COMPUTING DEVICES:
Edge computing is a type of distributed computing in which data is processed and stored at the edge of a network, closer to the user or device that is generating or requesting the data. Its use would enable creators and developers of metaverse applications to avoid intermittent connectivity issues with data. A single organization cannot develop the Metaverse. Like all successful initiatives, the Metaverse's success will result from a collaborative effort. This effort also includes increasingly powerful user devices that can share processing and connectivity workloads and data within their device capacity. A typical example of such a device is locally deployed Internet Exchanges (IXs)DE-CIX by DartPoints.
Smartphones/computer gadgets:
One of the cheapest and fastest ways to interact with VR/AR applications is through smartphone and personalized computer applications. Phone applications like Snapchat are daily AR software applications that can be easily accessed through smartphone or PC camera lenses as filtered pictures and videos.
Software Device or Application that supports the metaverse.
Artificial Intelligence (AI):
The simulating images and communicable voice rendition generated from Virtual Reality devices are AI-powered software applications. AI reasoning copies human-like intelligence categorically through the Sense, Comprehend and Act logic. The Technology programming of AI landscape mixes deep algorithms, natural language processing, and cognitive patterns. These landscapes are developed and deployed by software applications such as Unreal Engine, Unity, Blender, Cryengine, etc that aid in creating intelligent, responsive, and dynamic interactions within virtual environments active in the Metaverse.
Cloud Computing:
The practice of using a network of remote servers hosted on the internet to store, manage, and process data is known as cloud computing. Cloud Computing simplifies IT management and maintenance and provides better security, and enables faster remote proximity management of different servers across the Internet. Since the metaverse is said to be the next phase of the internet with a human-like experience, cloud computing supports larger numbers of processing power and storage interactions within the metaverse. Available cloud services like Amazon Web Service allow for faster relay of information and data across multiple demographics.
The internet of things (IoT):
The internet of things and cloud computing are interconnected and function simultaneously. IoT is simply a system that allows massive data to be generated, while cloud computing provides pathways for the generated data to travel to various destinations while keeping track of them. The usage of IoT in the metaverse will allow for seamless data extraction from the physical world and infuse it into the digital world. The collaboration with IoT will create digital twin replicas developers can work with to manifest and deploy characters that the metaverse needs. IoT software is GPS applications cars trackable across multiple layered devices like smartphones, smart television, smart watches, etc.
Bockchain Technology:
Blockchain technology is often referred to as the Motherboard. The metaverse promises to connect several users in a virtual environment to live, work, shop, and earn in a decentralized way. One of the key benefits of using blockchain technology in the metaverse is its ability to provide a secure and transparent platform for managing transactions and interactions within the virtual world. In addition to providing security and transparency, blockchain technology enables the creation of virtual assets like NFT and crypto currencies through smart contract development tradeable on exchanges supported by the metaverse and providing users with personalized peer-peer virtual experiences across multiple platforms.
Final thoughts
Researchers say extended reality technology present in the metaverse like VR and AR will surpass global game console shipments in 2024. These technologies will foster consumer adoption of metaverse and evolutionize the human digital experience in coming years. However, the Metaverse is not just a business opportunity. It is a new way of living. It is a game of humanity. A new way of being ourselves. A new way of interacting with the people and things around us, the digital world, and even the real world. A way of exploring, discovering, and building. As the future of the metaverse continues to evolve, these technologies will blend virtual and real-life content seamlessly into one another. Hence, the world of the Metaverse is virtual yet realistic to those who can build, use and demonstrate detailed articulations of their use cases.